
Advantages of Soil Stabilization in Agricultural Land Improvement
Soil stabilization refers to the process of improving the physical and chemical properties of land for agricultural purposes. It involves the use of various techniques and materials to enhance soil quality, stability, and productivity. Advances in soil stabilization have proven to be highly beneficial for farmers and the agricultural industry.
One of the main advantages of soil stabilization is its ability to prevent soil erosion. Agricultural land is often prone to erosion due to factors such as heavy rainfall, wind, and improper land management practices. By stabilizing the soil, farmers can reduce erosion and protect valuable topsoil from being washed or blown away. This helps to maintain the fertility of the land, improve water holding capacity, and prevent nutrient leaching.
Soil stabilization also improves the overall soil structure, making it more resistant to compaction. Compacted soil can restrict the root development of plants, leading to poor crop growth and yield. Through stabilization techniques, such as the addition of organic matter or amendments, farmers can enhance soil structure and porosity. This allows for better root penetration, nutrient uptake, and water infiltration, resulting in healthier plants and increased agricultural productivity.
Furthermore, soil stabilization plays a crucial role in reducing soil contamination and the leaching of pollutants into groundwater. Agricultural practices, such as the use of pesticides and fertilizers, can contribute to the presence of harmful chemicals in the soil. By stabilizing the soil, these contaminants can be immobilized or degraded, preventing their movement into water sources and minimizing the negative impact on the environment.
In conclusion, soil stabilization offers numerous benefits for agricultural land improvement. It helps prevent soil erosion, improves soil structure, and reduces contamination. By implementing soil stabilization techniques, farmers can enhance the sustainability and productivity of their land, contributing to the overall success of the agricultural industry.
Enhanced crop growth
Soil stabilization plays a crucial role in improving agricultural land and enhancing crop growth. By stabilizing the soil, farmers are able to create a more favorable environment for their crops to thrive.
One of the major advantages of soil stabilization is the improvement of nutrient availability in the land. The stabilization process helps to retain essential nutrients in the soil, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. This ensures that crops have access to all the necessary nutrients they need for optimal growth and development.
In addition, soil stabilization also helps to improve the water holding capacity of the land. By stabilizing the soil structure, it becomes more resistant to erosion and water runoff. This means that water is retained in the soil for longer periods, allowing crops to access the moisture they require for growth. This is especially important in dry regions or during periods of drought.
Furthermore, soil stabilization helps to regulate soil pH levels. This is crucial for crop growth, as different plants thrive in specific pH ranges. By stabilizing the soil, farmers can ensure that the pH levels remain within the desired range, providing an optimal growth environment for their crops.
Overall, soil stabilization offers numerous benefits for enhancing crop growth. It improves nutrient availability, increases water holding capacity, and regulates soil pH levels. By implementing soil stabilization techniques, farmers can create a thriving agricultural land that yields healthy and abundant crops.
Maintains nutrient levels
Soil stabilization techniques play a crucial role in maintaining nutrient levels in agricultural land. By stabilizing the soil, it helps to prevent the loss of essential nutrients that are vital for plant growth and development.
Agricultural land often faces challenges such as erosion, which can wash away valuable nutrients. However, by using soil stabilization methods, these nutrients can be effectively retained in the soil, ensuring their availability for crops.
One of the advantages of soil stabilization is that it helps to reduce nutrient runoff caused by excessive rainfall. When the soil is stable, it can better absorb and retain water, allowing it to infiltrate into the soil rather than being washed away, along with the nutrients, into nearby water bodies.
In addition, soil stabilization can also improve the nutrient-holding capacity of the soil. By enhancing the structure and composition of the soil, it increases its ability to hold onto essential nutrients, making them more accessible to plants.
Overall, the use of soil stabilization techniques in agricultural land improvement plays a vital role in maintaining nutrient levels. By preventing nutrient loss and enhancing nutrient-holding capacity, it helps to create a favorable environment for plant growth and ensures the continued productivity of the land.
Improves water retention
One of the key benefits of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is the improvement in water retention. Agricultural lands that have undergone stabilization processes have been found to have better water-holding capacity compared to untreated soils. This is advantageous for the growth and development of crops as it ensures a more consistent supply of water to the plants.
Soil stabilization techniques such as the addition of organic matter, use of cover crops, and application of soil amendments can help in enhancing the soil’s ability to retain water. These techniques promote the formation of stable soil aggregates, increase the soil’s ability to hold moisture, and reduce the risk of water runoff or soil erosion.
Improved water retention in stabilized agricultural land provides several advantages. Firstly, it helps to minimize water stress on crops during periods of drought or limited water availability. The plants can access water stored in the soil for longer periods, reducing the need for additional irrigation or water supplementation.
Secondly, improved water retention minimizes the risk of soil erosion and nutrient leaching. When the soil can retain water properly, it reduces the chances of water carrying away topsoil and essential nutrients, which are vital for the growth of crops. This promotes healthier soil conditions and ensures that nutrients are available for uptake by the plants.
| Improved water retention in stabilized agricultural land: |
| – Ensures a more consistent supply of water to the plants |
| – Minimizes water stress on crops during drought |
| – Reduces the risk of soil erosion and nutrient leaching |
Reduced soil erosion
One of the significant advantages of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is the reduction of soil erosion. Soil erosion refers to the process by which valuable topsoil is removed from the land surface due to wind or water. This can lead to numerous problems, including reduced soil fertility, nutrient loss, and decreased crop yields.
Soil stabilization techniques, such as the use of stabilizing agents or erosion control structures, can help prevent soil erosion by providing a stable surface for the soil particles. These techniques help to bind the soil particles together, making them less susceptible to erosion by wind or water. Additionally, soil stabilization can help improve the soil structure, making it more resistant to erosion.
By reducing soil erosion, agricultural land can maintain its productivity and sustainability over time. It helps to retain the valuable topsoil, which is essential for growing healthy crops. Furthermore, reduced soil erosion contributes to better water quality as it prevents sediment runoff into nearby water bodies.
Overall, soil stabilization plays a crucial role in agricultural land improvement by reducing soil erosion and promoting sustainable farming practices. By implementing soil stabilization techniques, farmers can protect their land, increase crop production, and contribute to environmental conservation.
Prevents runoff
One of the key benefits of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is its ability to prevent runoff. When land is stabilized, it becomes less prone to erosion and the loss of valuable topsoil. This is particularly important in agricultural settings where the land is regularly exposed to heavy rainfall or irrigation.
By preventing runoff, soil stabilization helps to retain moisture in the soil, which is vital for plant growth. It allows the water to penetrate the soil, keeping the land hydrated and reducing the need for additional irrigation. This is not only beneficial for the plants but also helps to conserve water resources.
Moreover, preventing runoff also helps to control sedimentation in nearby water bodies. When eroded soil is carried away by runoff, it can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic ecosystems. By stabilizing the soil and preventing erosion, agricultural activities can contribute to maintaining water quality and protecting the environment.
In addition, preventing runoff through soil stabilization can improve the overall productivity of agricultural land. When valuable topsoil is retained and protected, it provides a fertile and nutrient-rich environment for crops to grow. This enhances the overall yield of the agricultural land and promotes sustainable farming practices.
In conclusion, preventing runoff through soil stabilization brings numerous advantages for agricultural land improvement. It helps to retain moisture, conserve water resources, protect water bodies, and increase the productivity of the land. By implementing soil stabilization techniques, farmers can ensure the long-term sustainability and success of their agricultural operations.
Protects against wind erosion
One of the major advantages of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is that it helps protect against wind erosion. Wind erosion can be a significant problem in agricultural areas, as it can lead to the loss of fertile topsoil.
Soil stabilization techniques, such as the use of soil binders and erosion control blankets, can help prevent wind erosion by creating a protective layer on the soil surface. These techniques help to bind the soil particles together, making it more resistant to being blown away by strong winds.
In addition, soil stabilization can also help to improve the structure and stability of the soil, making it less prone to erosion. By increasing the cohesion of the soil particles, stabilization techniques can help to reduce the impact of wind and minimize the risk of erosion.
By protecting against wind erosion, soil stabilization can help to maintain the integrity of agricultural land and preserve the fertility of the soil. This can ultimately lead to higher crop yields and improved agricultural productivity.
| Advantages | Agricultural Land Improvement | Soil Stabilization | Protects against wind erosion |
Increased soil stability
One of the main benefits of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is increased soil stability.
Soil stabilization techniques, such as the use of stabilizing agents and compaction methods, help to improve the structural integrity and cohesion of the soil, making it more resistant to erosion and other forms of degradation.
Agricultural land is often subject to the erosive forces of wind and water, which can lead to soil erosion and loss of fertility. By stabilizing the soil, farmers can mitigate the risk of erosion and maintain the productivity of their land.
Stabilized soil has improved water holding capacity, allowing for better moisture retention and drainage. This is especially important in areas with irregular rainfall patterns, as it helps to prevent runoff and ensures that the soil has adequate moisture for plant growth.
In addition to preventing erosion and improving water management, stabilized soil also provides a stable base for agricultural activities. It helps to reduce soil compaction, making it easier for roots to penetrate and access nutrients. This leads to healthier and more productive crops.
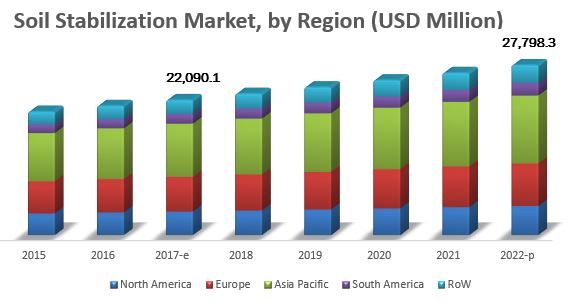
Overall, increased soil stability through soil stabilization techniques is crucial for agricultural land improvement. It helps to protect the land from erosion, improves water management, and provides a solid foundation for crop growth, resulting in improved yields and sustainable farming practices.
Prevents soil compaction
Soil stabilization has several advantages when it comes to improving agricultural land, one of which is preventing soil compaction. Compacted soil occurs when the soil particles are pressed together, reducing pore space and restricting the movement of air, water, and nutrients within the soil.
Soil compaction can negatively impact crop growth and development. When the soil is compacted, plant roots struggle to penetrate it, resulting in reduced access to essential nutrients and water. This can lead to stunted growth, decreased yields, and potential crop failure.
However, by implementing soil stabilization techniques, agricultural land can be protected from compaction. Stabilization methods such as the addition of organic matter, like compost or cover crops, improve soil structure and create a more stable environment for plant growth.
Moreover, the use of soil stabilization also promotes better water infiltration and drainage, preventing excessive runoff and erosion. This allows for efficient irrigation and reduces the risk of waterlogged soil.
Overall, preventing soil compaction through soil stabilization enhances the quality of agricultural land, ensuring optimal conditions for crop growth, and improving yields and profitability for farmers.
Minimizes soil settling
One of the significant advantages of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is that it minimizes soil settling. Soil settling occurs when soil particles shift and compact over time, leading to unstable ground conditions. This settling can cause a range of issues for agricultural land, including uneven surfaces, poor drainage, and reduced fertility.
By implementing soil stabilization techniques, such as adding stabilizing agents or reinforcing materials, the soil’s structural integrity is improved. These methods help to bind the soil particles together, preventing excessive settling. As a result, agricultural land can maintain a more even surface, allowing machinery to operate smoothly and reducing the risk of damage.
In addition to minimizing soil settling, soil stabilization also provides benefits such as increased load-bearing capacity, improved water infiltration, and reduced erosion. These advantages contribute to the long-term health and productivity of agricultural land, ensuring optimal conditions for crop growth and sustainability.
Enhanced soil structure
One of the key advantages of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is the enhancement of soil structure. This is crucial for the overall health and productivity of the land.
Soil stabilization techniques, such as the use of soil stabilizers and binders, help to improve the physical properties of the soil. By stabilizing the soil, it becomes less prone to erosion, compaction, and other forms of degradation.
Enhanced soil structure allows for better water infiltration and retention, promoting optimal moisture levels for plant growth. It also improves root penetration, allowing plants to access essential nutrients and minerals from deeper layers of the soil.
Moreover, an enhanced soil structure helps to create a more stable foundation for agricultural activities. This reduces the risk of machinery sinking into the soil and causing damage, as well as prevents the formation of ruts and uneven surfaces.
Overall, the improved soil structure resulting from soil stabilization techniques is an essential factor in agricultural land improvement. It ensures the health and productivity of the land, allowing for enhanced crop growth and yields.
Promotes root development
One of the advantages of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is that it promotes root development. By stabilizing the soil, farmers can create a more conducive environment for plant roots to grow and spread.
When soil is unstable or compacted, it can hinder root growth and cause issues such as poor nutrient uptake, restricted water absorption, and limited access to oxygen. This can significantly affect the health and productivity of agricultural crops.
Soil stabilization techniques, such as the addition of organic matter, can improve the structure and composition of the soil, making it easier for roots to penetrate and expand. This results in stronger, deeper root systems that can better anchor plants and access essential nutrients and water.
In addition to enhancing root development, stabilized soil also helps in reducing erosion, minimizing the risk of land degradation, and improving overall soil fertility. These factors contribute to the overall improvement of agricultural land, leading to higher crop yields and healthier plant growth.
| Promotes root development |
| Reduces erosion |
| Minimizes the risk of land degradation |
| Improves soil fertility |
Improves soil aeration
Soil stabilization offers significant advantages in improving soil aeration. A well-aerated soil is crucial for plant growth as it ensures the proper exchange of gases between the soil and the atmosphere. By stabilizing the soil, the pore spaces in the land are increased, allowing for better air circulation. This aeration process enhances the soil’s ability to retain moisture and nutrients, promoting healthier crop growth.
Decreased soil contamination
One of the major advantages of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is the decreased soil contamination. Contaminated soil poses a serious risk to agricultural practices as it can negatively impact crop growth and yield. Through soil stabilization techniques, such as the addition of stabilizing agents or the implementation of erosion control measures, the level of soil contamination can be significantly reduced.
Soil stabilization helps to prevent the spread of contaminants by creating a barrier between the soil and the contaminants. This barrier prevents the contaminants from leaching into the soil and reaching the crops. Additionally, stabilized soil can help in the remediation process by immobilizing contaminants and preventing their movement.
The decreased soil contamination achieved through soil stabilization techniques not only improves the quality of the agricultural land but also promotes the overall health and safety of both the environment and the consumers of agricultural products. It enables farmers to grow healthy crops and reduces the risk of contamination-related diseases.
In conclusion, soil stabilization is a valuable tool for agricultural land improvement as it effectively decreases soil contamination. By implementing soil stabilization techniques, farmers can ensure the productivity and sustainability of their land, and contribute to a healthier and safer environment.
Prevents leaching of pollutants
One of the key advantages of soil stabilization for agricultural land improvement is its ability to prevent the leaching of pollutants. When land is improved through soil stabilization techniques, such as the addition of stabilizing agents or the use of erosion control measures, the soil becomes more resistant to erosion and runoff.
This improved soil stability helps to prevent the leaching of pollutants, such as fertilizers, pesticides, and other chemicals, into nearby water sources. When these pollutants are allowed to leach into water sources, they can contaminate drinking water supplies and harm aquatic ecosystems. By preventing leaching, soil stabilization helps to protect the environment and ensure the sustainability of agricultural practices.
Soil stabilization techniques can also help to prevent the leaching of pollutants into the soil itself. When pollutants are allowed to leach into the soil, they can degrade its quality and make it less fertile. This can have a negative impact on crop yields and overall agricultural productivity.
By stabilizing the soil, farmers can create a more favorable environment for plant growth and ensure the long-term health and productivity of their land. This improved soil stability also reduces the need for excessive application of fertilizers and other agrochemicals, leading to cost savings and a more sustainable agricultural system.
In conclusion, soil stabilization plays a crucial role in preventing the leaching of pollutants, both into water sources and the soil itself. This has numerous benefits for agricultural land improvement, including environmental protection, enhanced crop productivity, and cost savings for farmers.
Frequently asked questions:
What is soil stabilization?
Soil stabilization is the process of improving the properties of soil to make it suitable for agricultural purposes. It involves adding materials or implementing techniques to enhance the strength, durability, and fertility of the soil.
What are the benefits of soil stabilization for agricultural land?
Soil stabilization offers numerous benefits for agricultural land improvement. First, it helps prevent soil erosion by making the soil more compact and resistant to water and wind erosion. Additionally, it improves soil fertility by enhancing nutrient retention and water holding capacity. This, in turn, promotes better plant growth and yield. Stabilized soil also has improved load-bearing capacity, making it suitable for supporting heavy machinery and equipment needed for farming activities.
How does soil stabilization help in preventing soil erosion?
Soil stabilization plays a crucial role in preventing soil erosion. By adding stabilizing agents such as lime or cement, the soil is made more compact and less prone to erosion caused by heavy rainfall or wind. These agents bind the soil particles together, creating a stronger and more stable structure that can withstand the erosive forces. Additionally, stabilized soil absorbs water more effectively, reducing the chances of runoff and erosion.
What are some commonly used materials for soil stabilization?
There are various materials that can be used for soil stabilization. Popular options include cement, lime, fly ash, and bitumen. Cement and lime are commonly used for stabilizing clayey soils, while fly ash is often used for sandy or silty soils. Bitumen, a sticky and viscous material, is used primarily for stabilizing roads and pavements.
Can soil stabilization improve crop yields?
Yes, soil stabilization can indeed improve crop yields. By enhancing soil fertility and water retention, stabilized soil provides an ideal environment for plant growth. The improved nutrient availability allows plants to thrive and produce higher yields. Additionally, the increased load-bearing capacity of stabilized soil allows for efficient use of agricultural machinery, facilitating timely farming operations and ultimately contributing to better crop yields.
What is soil stabilization?
Soil stabilization is a technique used to improve the physical properties of soil, making it more suitable for agricultural purposes. It involves the addition of materials or chemicals to the soil to enhance its strength, durability, and resistance to erosion.
Why is soil stabilization important for agricultural land improvement?
Soil stabilization is important for agricultural land improvement because it helps to increase the productivity and sustainability of the land. By stabilizing the soil, farmers can prevent soil erosion, improve water infiltration, and enhance the nutrient-holding capacity of the soil, thus creating a more favorable environment for plant growth.





