Understanding Soil Compaction: Its Causes, Challenges, and Effective Solutions
Soil compaction is a common problem that affects both urban and rural areas, and it can have significant impacts on the health of plants and the environment. Compaction occurs when soil particles are pressed together, reducing pore spaces and limiting the movement of air, water, and nutrients. This phenomenon can be caused by a variety of factors, including heavy machinery, excessive foot traffic, and improper land management practices.
One of the challenges of soil compaction is that it can be difficult to detect. The effects may not be immediately visible, but over time, compacted soil can lead to poor drainage, increased erosion, and reduced plant growth. Compacted soil also has a lower capacity to hold water, which can result in waterlogged conditions and inhibit root development. Furthermore, compaction can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms in the soil, affecting nutrient cycling and overall soil health.
So, what can be done to prevent and address soil compaction? There are a few solutions that landowners and farmers can implement. First and foremost, it is important to avoid unnecessary soil disturbance and limit the use of heavy machinery on the land. Additionally, implementing proper land management practices, such as rotating crops, using cover crops, and reducing tillage, can help improve soil structure and reduce compaction.
Another effective solution is the use of soil amendments, such as organic matter and gypsum, which can help improve the structure and drainage of compacted soil. These amendments can be incorporated into the soil to enhance its ability to hold water and provide a conducive environment for root growth. In some cases, soil aeration techniques, such as deep tillage or subsoiling, can be used to alleviate compaction and restore soil health.
In conclusion, soil compaction is a significant issue that can have detrimental effects on plant growth and overall soil health. Understanding the causes, challenges, and solutions to soil compaction is crucial for sustainable land management and agriculture. By implementing proper practices and using effective solutions, we can help prevent and address soil compaction, ensuring the long-term health and productivity of our soils.
Understanding Soil Compaction
Soil compaction is a common problem that affects agricultural and gardening practices. It occurs when the soil particles are compressed, reducing pore space and making it difficult for plant roots to penetrate and extract nutrients. Understanding the causes and challenges of soil compaction is crucial in finding effective solutions.
The causes of soil compaction can vary, but the most common factors include heavy machinery and equipment used in farming, construction, and landscaping. The weight and repeated traffic of these machines can compress the soil, creating compacted layers. Additionally, excessive moisture or rainfall can also contribute to soil compaction.
Knowing more about soil properties is essential in understanding the challenges associated with soil compaction. Soil compaction can lead to poor water drainage, increased runoff, erosion, and reduced nutrient availability for plants. These challenges can negatively impact crop yields and plant health.
Understanding why soil compaction occurs can help in devising suitable solutions. Proper soil management practices such as minimizing heavy machinery traffic, avoiding excessive soil moisture, and incorporating organic matter can help prevent or alleviate soil compaction. Implementing techniques like deep tillage and subsoiling can also help loosen compacted soil layers.
All in all, understanding soil compaction is crucial in promoting healthy soil and ensuring optimal plant growth. By identifying the causes and challenges, along with implementing effective solutions, we can achieve better soil quality and productivity.
Definition and Importance
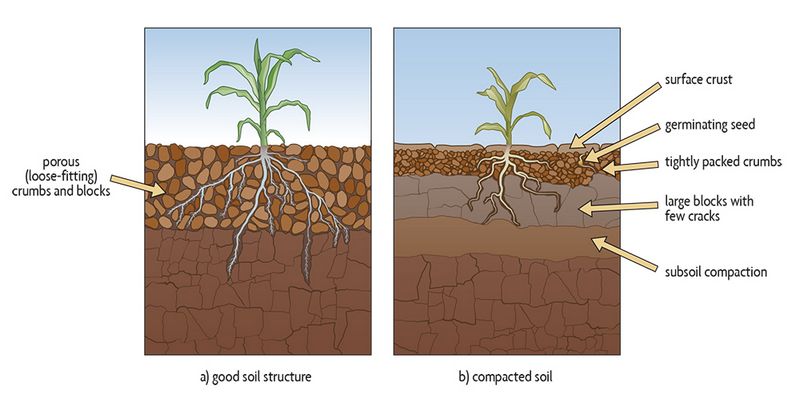
Soil compaction refers to the process by which the soil particles are compressed and compacted, resulting in reduced pore space between them. This reduces the ability of the soil to hold water, nutrients, and air, and restricts root growth.
All soils, regardless of their type, can experience compaction. It can be caused by natural factors, such as rainfall or the weight of vehicles, as well as human activities, such as construction or agriculture.
Soil compaction poses several challenges. Firstly, it reduces the soil’s ability to absorb and retain water, leading to increased runoff and soil erosion. Secondly, it hampers the movement of air within the soil, which negatively affects soil respiration and the growth of soil organisms. Lastly, compaction limits root penetration, impairing plant growth and productivity.
The importance of addressing soil compaction cannot be overstated. Compacted soils have a negative impact on agricultural productivity, as they result in poor crop growth and reduced yields. In addition, compacted soils are more prone to flooding and erosion, which can further degrade the soil quality.
Fortunately, there are several solutions to mitigate soil compaction. The first step is to identify the causes of compaction and modify practices accordingly. For example, reducing the frequency and intensity of vehicular traffic or implementing controlled traffic systems can help minimize compaction. Another approach is by implementing proper soil management techniques, such as organic amendments or cover cropping, to improve soil structure and increase its resistance to compaction.
In conclusion, soil compaction is a serious issue that has negative consequences for soil health and agricultural productivity. Understanding the causes, challenges, and potential solutions to soil compaction is crucial in preserving the quality and fertility of soils for sustainable agriculture.
Effects on Plant Growth
Soil compaction can have significant negative effects on plant growth. When soil compaction occurs, the soil particles become packed together tightly, reducing the pore space and restricting the movement of air, water, and roots.
This restriction can lead to a decrease in oxygen availability for the roots, which is essential for various metabolic processes, including the uptake of water and nutrients. Without sufficient oxygen, root development can be stunted and nutrient uptake can be impaired.
In addition, compacted soil makes it difficult for roots to push through the soil, limiting their ability to grow and explore for resources. This can result in reduced root biomass and a shallower root system, which makes plants more susceptible to drought stress.
Furthermore, soil compaction can affect soil structure, leading to poor drainage. When the soil is compacted, water is unable to penetrate effectively, causing excessive runoff and soil erosion. The lack of water infiltration can also lead to moisture stress for plants, as they are not able to access the water that is present.
In summary, soil compaction causes all of these challenges, ultimately leading to a decline in plant growth and overall health. It is important to understand the effects of soil compaction so that appropriate measures can be taken to mitigate or prevent it, such as avoiding heavy machinery on soil when it is wet, practicing proper soil management techniques, and implementing regular soil testing and monitoring.
Causes of Soil Compaction
Soil compaction refers to the compression or reduction in the volume of soil, resulting in the soil becoming denser and more tightly packed. There are several factors that can contribute to soil compaction, and understanding these causes is essential in order to effectively address the challenges it presents.
- Heavy Machinery: The use of heavy machinery, such as tractors, bulldozers, and excavators, can cause soil compaction. The weight and repetitive movement of these machines can significantly compact the soil, making it less porous and limiting the movement of air and water through the soil profile.
- Foot Traffic: Allowing excessive foot traffic, especially on wet or saturated soils, can lead to compaction. The pressure and movement of people or animals on the soil surface can compact the soil particles, reducing pore space and disrupting the natural structure of the soil.
- Improper Tillage: Improper tillage practices, such as using equipment with inadequate depth settings or working the soil when it is too wet, can contribute to soil compaction. Incorrect tillage techniques can result in the compaction of the soil layers and the formation of compacted zones.
- Excessive Watering: Overwatering or improper irrigation practices can also cause soil compaction. Excess water in the soil can lead to saturation and the loss of soil structure, resulting in increased compaction.
- Soil Type: The type of soil plays a significant role in its susceptibility to compaction. Fine-textured soils, such as clay, are more prone to compaction than coarse-textured soils, like sandy soils. This is due to the smaller size of the particles in fine-textured soils, which makes them more easily compacted.
Understanding the causes of soil compaction is crucial for developing effective solutions and taking preventive measures. By addressing the factors that contribute to soil compaction, such as avoiding excessive machinery use, managing foot traffic, implementing proper tillage practices, and maintaining proper irrigation, soil compaction can be minimized, allowing for better soil health and productivity.
Heavy Machinery
When we talk about soil compaction, heavy machinery is often one of the main causes. These large and powerful machines can cause significant compaction of the soil, leading to a variety of challenges.
One of the main reasons heavy machinery contributes to soil compaction is its sheer weight. The heavy vehicles and equipment exert a tremendous amount of pressure on the ground, causing the soil particles to become densely packed. This can result in reduced water infiltration, poor root growth, and limited nutrient availability for plants.
Additionally, the repeated use of heavy machinery in the same area can further exacerbate soil compaction. Each time the equipment passes over the soil, it compacts the already compacted soil even more. This can create highly compacted layers within the soil profile, which can be difficult to break up and can negatively impact plant health.
Considering the challenges heavy machinery poses, it is important to implement solutions to mitigate soil compaction. One solution is to limit the use of heavy machinery in areas where compaction is a concern. This can be achieved by implementing alternative construction methods or using lighter equipment when possible.
Another solution is to implement soil management practices that help improve soil structure and reduce compaction. This can include regular soil testing to monitor compaction levels, aerating the soil to promote air and water movement, and adding organic matter to improve soil quality.
Overall, understanding the causes, challenges, and solutions to soil compaction caused by heavy machinery is essential for sustainable land management practices. By being aware of the impacts of heavy machinery on soil health, we can work towards protecting and preserving one of our most valuable natural resources.
Foot and Vehicle Traffic
One of the major causes of soil compaction is foot and vehicle traffic. When people or vehicles repeatedly traverse the same area, the weight and pressure they exert can cause the soil particles to become tightly packed together. This compression reduces the space between the particles, making it difficult for air, water, and roots to move freely through the soil.
This compaction can lead to a range of challenges and issues. Firstly, it can reduce soil porosity, which affects the soil’s ability to drain properly. With reduced pore space, water can accumulate on the surface, causing flooding and waterlogged conditions. This, in turn, can lead to problems such as drowning of plant roots and increased susceptibility to diseases.
Furthermore, compacted soil can inhibit root growth and penetration. The tightly packed particles restrict the movement and elongation of roots, making it harder for plants to establish a strong root system and access essential nutrients and water. This results in stunted growth, reduced vigor, and diminished crop yields.
To address the challenges associated with foot and vehicle traffic, various solutions can be implemented. One effective measure is to limit or redirect traffic in heavily trafficked areas. By creating designated paths or roads, the impact on the soil can be spread out and concentrated in specific areas, minimizing compaction on the rest of the land.
Implementing technologies such as grids, geotextiles, or reinforced structures can also help distribute the weight, reducing the pressure on the soil. These solutions can be especially useful for areas that experience frequent heavy machinery or vehicle use.
Additionally, it is important to regularly monitor soil compaction levels and take proactive measures to mitigate the problem. A soil compaction test, such as a penetrometer or soil compaction meter, can be used to assess the soil’s density and compaction levels. Based on the results, appropriate measures, such as deep tillage or soil aeration, can be undertaken to alleviate compaction and improve soil health.
Overall, foot and vehicle traffic can significantly contribute to soil compaction. Understanding the causes, challenges, and potential solutions to this issue is crucial for maintaining healthy soil and promoting optimal plant growth.
Improper Agriculture Practices
Improper agriculture practices are one of the main causes of soil compaction. Farmers who do not use proper techniques or tools when working in the field can inadvertently cause soil compaction. This is especially true when heavy machinery is used, such as tractors or combines, which can exert a lot of pressure on the soil.
There are several challenges associated with improper agriculture practices that lead to soil compaction. One challenge is the use of heavy machinery without proper consideration of soil moisture levels. When the soil is too wet, the machinery can easily compact the soil, making it more difficult for plants to grow. Similarly, when the soil is too dry, machinery can also cause compaction by exerting too much pressure on the soil.
Another challenge is the lack of crop rotation or cover cropping. When the same crop is grown year after year, it can lead to soil compaction. This is because certain crops have deep root systems that help to break up compacted soil. Without crop rotation or cover cropping, the soil can become more compacted over time.
One solution to address the challenges posed by improper agriculture practices is to use conservation tillage techniques. Conservation tillage involves minimizing the amount of disturbance to the soil during planting and other farming operations. This can help to reduce compaction by preserving the natural structure of the soil.
Another solution is to use proper timing and equipment when working in the field. Farmers should be aware of soil moisture levels and only work the soil when it is at the appropriate moisture content. Additionally, using lighter machinery or equipment with larger tires can help to minimize soil compaction.

In conclusion, improper agriculture practices can lead to soil compaction, which poses challenges for farmers. It is important for farmers to be aware of the causes of compaction and take steps to prevent it. By using conservation tillage techniques and being mindful of soil moisture levels and equipment choice, farmers can effectively address the issues associated with soil compaction.
Challenges of Soil Compaction
Soil compaction is a significant issue that affects agricultural, construction, and gardening industries. Understanding the challenges associated with soil compaction is crucial for identifying effective solutions. Here’s what you need to know:
About Soil Compaction:
Soil compaction refers to the compression of soil particles, which leads to a decrease in the volume of pore spaces. This compression reduces the ability of the soil to hold water, nutrients, and air, which can have detrimental effects on plant growth and soil health. Compacted soil is denser and harder, making it difficult for roots to penetrate and grow.
Why Soil Compaction Occurs:
Soil compaction can occur due to various factors, including heavy machinery, livestock trampling, excessive foot traffic, and improper soil management practices. When machinery or animals exert pressure on the soil, the particles become tightly packed, resulting in compaction. Additionally, the compaction process can be accelerated by improper tillage techniques and over-irrigation.
Challenges of Soil Compaction:
The challenges associated with soil compaction are numerous and include:
1. Reduced Drainage:
Compacted soil has limited pore spaces, which restricts water drainage. This can lead to poor water infiltration and increased surface runoff, causing erosion and nutrient loss.
2. Decreased Aeration:
Compaction reduces the amount of airspace within the soil, limiting the movement of oxygen into the root zone. Lack of proper aeration can hinder root respiration and nutrient uptake, negatively affecting plant health.
3. Impaired Root Growth:
The compacted soil structure inhibits root penetration and restricts root elongation. This results in shallow, weak root systems that are more susceptible to drought stress and nutrient deficiencies.
4. Decreased Yield Potential:
Compacted soil affects the overall productivity of plants by limiting root development, nutrient availability, and water infiltration. This can lead to reduced crop yields and lower quality produce.
Potential Solutions:
Addressing challenges associated with soil compaction requires implementing effective solutions, such as:
1. Soil Aeration:
Aerating the soil through mechanical means or natural processes can help alleviate compaction by improving airflow and promoting healthy root development.
2. Organic Matter Addition:
Incorporating organic matter, such as compost or manure, into the soil can improve its structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability, reducing the risk of compaction.
3. Corrective Tillage:
Proper tillage practices, such as deep ripping or subsoiling, can help break up compacted layers and improve soil structure for better water and root penetration.
4. Crop Rotation and Cover Crops:
Implementing crop rotation and cover cropping techniques can help improve soil health and structure, reduce compaction, and enhance overall soil fertility.
By understanding the challenges associated with soil compaction and implementing appropriate solutions, it is possible to mitigate the negative impacts and promote healthy soil for optimal plant growth and productivity.
Reduced Water Infiltration
Soil compaction poses numerous challenges for the agricultural industry, and one major concern is reduced water infiltration. Understanding what causes this issue and why it is important to address it can help farmers and land managers effectively combat soil compaction.
Causes of reduced water infiltration are directly related to soil compaction. When soil becomes compacted, its pore spaces shrink, limiting the movement of air and water in the soil profile. This compaction can occur from heavy machinery or livestock trampling the soil, excessive tillage practices, or improper land management techniques.
Water infiltration is a critical aspect of soil health. It determines how well water can penetrate the soil and be stored for plant use. When water infiltration is restricted due to soil compaction, several detrimental effects can occur. First, excess water can accumulate on the soil surface, leading to waterlogging and increased runoff. This can result in nutrient leaching, loss of soil fertility, and erosion.
Furthermore, reduced water infiltration can impede root growth and development. Plant roots require oxygen for respiration and nutrient uptake, both of which are limited in compacted soil. As a result, plants may struggle to establish a healthy root system and may experience stunted growth or decreased yield.
To address the challenges posed by reduced water infiltration due to soil compaction, various solutions can be implemented. One approach is to minimize the use of heavy machinery on wet or saturated soils to prevent compaction. Additionally, using appropriate tillage techniques, such as reduced tillage or no-till practices, can help preserve soil structure and minimize compaction.
Implementing soil conservation practices like cover cropping and crop rotation can also improve soil health and reduce compaction. Cover crops help improve soil structure and increase organic matter content, leading to improved water infiltration. Crop rotation allows for the diversification of root systems and minimizes the risk of soil compaction caused by repetitive planting of the same crop.
In conclusion, reduced water infiltration is a significant consequence of soil compaction. Understanding the causes and effects of this issue allows farmers and land managers to take proactive steps in combating soil compaction, ensuring optimal soil health and crop productivity.
Frequently asked questions:
What is soil compaction?
Soil compaction refers to the process where soil particles are compressed, reducing the pore spaces between them. This leads to decreased porosity, increased soil density, and reduced air and water movement in the soil.
What causes soil compaction?
Soil compaction can be caused by various factors including heavy machinery or equipment traffic, excessive tillage, repeated foot or vehicle traffic, and the use of improper soil management techniques.
What are the challenges of soil compaction?
Soil compaction can lead to reduced crop yields as it restricts root growth and penetration, limits the availability of air and water in the soil, and increases the susceptibility of plants to diseases and pests. It can also cause soil erosion and runoff, further impacting the overall health of the ecosystem.
What are some solutions to soil compaction?
There are several solutions to soil compaction including practicing proper soil management techniques such as reduced tillage or no-till farming, avoiding excessive machinery traffic, using cover crops to improve soil structure, and incorporating organic matter into the soil. Additionally, implementing soil conservation practices like contour plowing and terracing can also help prevent soil compaction.
How can we prevent soil compaction?
To prevent soil compaction, it is important to avoid excessive foot or vehicle traffic on the soil, especially when it is wet or moist. Implementing proper soil management practices like avoiding over-tilling and reducing the use of heavy machinery can also help prevent soil compaction. Additionally, maintaining a healthy soil structure through the incorporation of organic matter and the use of cover crops can contribute to preventing soil compaction.
What is soil compaction?
Soil compaction refers to the process in which soil particles are compressed and packed together, reducing the pore space and air pockets within the soil.






