Common Methods of Hazardous Waste Disposal
The issue of hazardous waste disposal is a critical environmental concern worldwide. Ensuring the safe and environmentally friendly disposal of hazardous waste is essential to protect human health and the environment. There are several common methods that are used to dispose of hazardous waste effectively. These methods include deep-well injection, incineration, disposal in landfills, neutralization, and recycling.
Deep-well injection involves injecting hazardous waste deep underground into approved wells. This method is often used for the disposal of liquid hazardous waste, such as industrial wastewater or chemical sludge. The waste is injected into geological formations that are designed to contain and isolate the waste from the surrounding environment.
Incineration is another commonly used method for hazardous waste disposal. It involves burning the waste at high temperatures to reduce its volume and convert it into less harmful byproducts. Incineration can be an effective way to dispose of solid, liquid, or gaseous hazardous waste. However, it is important to ensure that the incineration facility is properly designed and operated to prevent air pollution and the release of toxic emissions.
Disposing of hazardous waste in landfills is a widely used method, especially for solid or semi-solid waste. The waste is placed in designated areas of landfills that are specially engineered to prevent the leakage of hazardous substances into the soil and groundwater. However, proper management and monitoring are crucial to ensure that landfills do not pose a significant risk to human health and the environment.
Another method of hazardous waste disposal is neutralization, which involves treating the waste with chemicals to make it less harmful or non-toxic. This method is commonly used for liquid waste that contains corrosive or acidic substances. By neutralizing the waste, it can be rendered safe for further treatment or disposal.
Finally, recycling is an important method of hazardous waste disposal that aims to minimize the amount of waste that needs to be disposed of and reduce the environmental impact. Recycling involves the reprocessing of waste materials to extract valuable resources or convert them into new products. This method can be particularly effective for hazardous waste, as it helps to conserve natural resources and reduce the demand for raw materials.
In conclusion, the proper disposal of hazardous waste is crucial to protect human health and the environment. Deep-well injection, incineration, landfill disposal, neutralization, and recycling are common methods used to ensure safe and environmentally friendly solutions. Each method has its advantages and considerations, and the choice of disposal method depends on the type and characteristics of the hazardous waste. Implementing effective waste management practices is essential to ensure a sustainable and cleaner future.
Understanding Hazardous Waste Disposal
Hazardous waste disposal refers to the process of safely and responsibly getting rid of waste materials that are dangerous to human health and the environment. Hazardous waste can come in various forms, including chemicals, heavy metals, radioactive materials, and other harmful substances. It is essential to handle and dispose of such waste properly to prevent contamination and potential harm to living organisms and ecosystems.
There are several methods available for the disposal of hazardous waste, each with its own advantages and limitations. These methods include:
- Neutralization: This method involves treating hazardous waste with chemicals to make it less dangerous or non-hazardous. Neutralization is commonly used for liquid waste, such as acids or bases, to adjust their pH levels and minimize their toxicity.
- Landfill: Landfill disposal involves burying hazardous waste in a specially designed landfill facility. The waste is placed in designated areas and covered with layers of soil or other barrier materials to prevent leakage and contamination of groundwater. Landfills must meet strict regulations and monitoring requirements to ensure the safe containment of hazardous waste.
- Deep-Well Injection: Deep-well injection involves injecting hazardous waste deep into the ground, typically below the water table. This method is suitable for liquid waste that cannot be easily treated or disposed of by other means. The waste is injected into a well, isolated by impermeable rock layers, preventing migration and potential contamination of groundwater.
- Recycling: Recycling hazardous waste involves transforming it into a reusable product or recovering valuable materials. This method helps reduce the amount of waste generated and conserves resources. It is commonly used for certain types of hazardous waste, such as batteries, electronic waste, and certain chemicals.
- Incineration: Incineration involves burning hazardous waste at high temperatures in specially designed facilities. The process helps reduce the volume of waste and destroy harmful compounds. However, incineration can release pollutants into the air if not properly controlled and monitored.
It is important to evaluate the characteristics of hazardous waste and choose the most appropriate disposal method based on factors such as toxicity, volume, and cost considerations. Additionally, strict regulations and guidelines are in place to govern the handling, transportation, and disposal of hazardous waste to minimize environmental and health risks.
Importance of Safe Disposal Methods
Hazardous waste is a serious threat to both human health and the environment. It contains substances that can be harmful or toxic, and if not properly managed, it can contaminate air, water, and soil, leading to serious consequences.
Safe disposal methods are essential for managing hazardous waste effectively. They help minimize the risks associated with these materials and protect both human health and the environment. Here are some reasons why safe disposal methods are important:
- Preventing contamination: Safe disposal methods, such as recycling, incineration, and landfill, ensure that hazardous waste is managed in a way that prevents contamination of air, water, and soil. By following proper procedures, harmful substances can be contained and prevented from entering the environment.
- Protecting human health: Hazardous waste can have severe health effects if not handled and disposed of safely. Exposure to toxic substances can lead to acute or chronic illnesses, respiratory problems, organ damage, and even cancer. By using safe disposal methods, the risks to human health can be minimized or eliminated.
- Promoting sustainability: Safe disposal methods often involve recycling or reusing hazardous waste. This reduces the demand for raw materials and conserves natural resources. It also helps reduce the amount of waste being sent to landfills or incinerators, promoting a more sustainable approach to waste management.
- Complying with regulations: Many countries have strict regulations and guidelines for the proper disposal of hazardous waste. Safe disposal methods ensure compliance with these regulations, avoiding legal consequences and penalties.
- Minimizing environmental impact: Hazardous waste can have severe and long-lasting impacts on the environment. It can contaminate water sources, harm wildlife, and disrupt ecosystems. Safe disposal methods help minimize these impacts by preventing the release of hazardous substances into the environment.
Overall, safe disposal methods are crucial in managing hazardous waste effectively. They protect human health, prevent contamination, promote sustainability, comply with regulations, and minimize environmental impact. By implementing these methods, we can ensure a safer and more environmentally friendly approach to handling hazardous waste.
Landfilling: A Traditional Method

Landfilling is one of the most commonly used methods for hazardous waste disposal. It involves the burial of waste materials in specially designated areas called landfills. This method has been used for many years and is considered a traditional approach to waste management.
Hazardous waste that is not suitable for incineration, neutralization, or other treatment methods is often sent to landfills for final disposal. Landfills for hazardous waste have strict regulations and requirements to ensure that the waste is contained and does not pose a threat to the environment or public health.
In a hazardous waste landfill, the waste is placed in carefully engineered cells or pits. These cells are lined with impermeable materials such as clay or synthetic liners to prevent the leakage of hazardous substances into the surrounding soil and groundwater.
Landfills for hazardous waste are typically divided into different zones to accommodate different types of waste. This allows for better organization and management of the waste, as well as easier monitoring and inspection.
One type of hazardous waste landfill is the deep-well landfill. This method involves injecting the waste into deep underground wells, where it is isolated from the environment. The waste is usually mixed with a solidifying agent to immobilize it and prevent migration.
Landfilling is considered a cost-effective method for hazardous waste disposal, as it requires less energy and resources compared to other methods such as incineration. However, it is important to note that landfills are not a permanent solution. Over time, they can become full and may need to be closed and monitored to ensure long-term environmental safety.
Overall, landfilling remains a widely used method for hazardous waste disposal, providing a safe and controlled environment for the containment of hazardous materials. However, efforts are constantly being made to develop more sustainable and environmentally friendly methods for the management of hazardous waste.
Incineration: Disposing Through Combustion
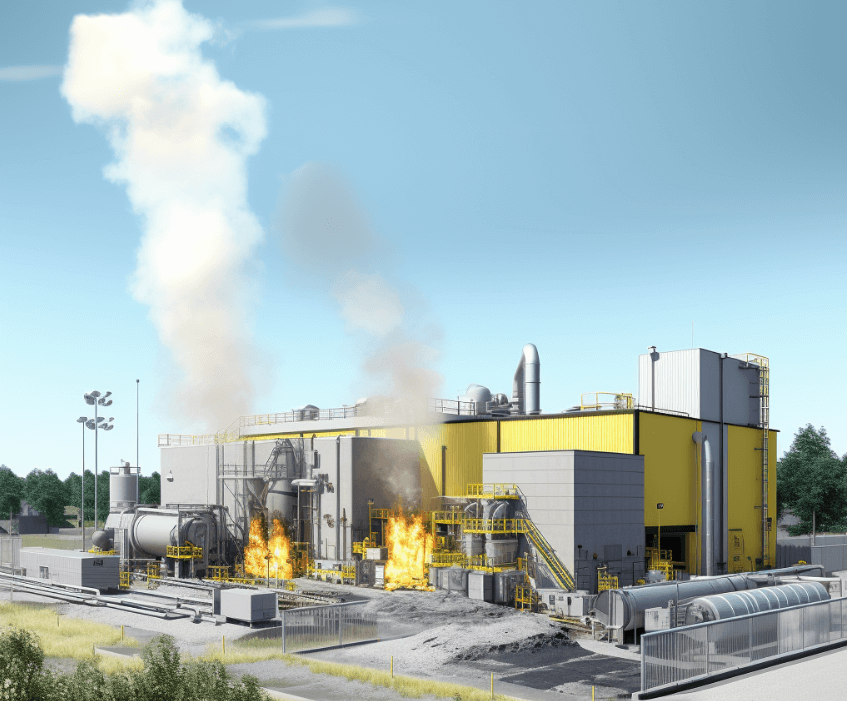
Incineration is one of the most commonly used methods for hazardous waste disposal. It involves the combustion of waste materials at very high temperatures, typically ranging from 800 to 1,200 degrees Celsius. This process helps reduce the volume of waste and convert it into non-hazardous substances.
Incineration offers several advantages over other disposal methods. Firstly, it can effectively destroy hazardous materials, including toxic chemicals and infectious agents, minimizing their potential harm to human health and the environment. Additionally, incineration can be a more environmentally friendly option compared to other methods such as landfilling, as it reduces the amount of waste that needs to be stored long-term.
During the incineration process, hazardous waste is burned in specially designed furnaces or incinerators. These facilities have advanced air pollution control systems to prevent the release of harmful gases and particulate matter into the atmosphere. This helps to minimize the potential impact on air quality and reduce the emission of greenhouse gases.
Incineration can be further enhanced by implementing waste-to-energy technologies. In this approach, the heat generated from the combustion process is captured and used to produce electricity or heat. This turns the waste into a valuable resource and reduces the reliance on fossil fuels for energy production.
However, incineration also has its limitations and challenges. High costs associated with building and operating incineration facilities can be a barrier to implementation. The potential release of toxic air pollutants, such as dioxins and heavy metals, is a concern that must be carefully managed through stringent emission control measures.
Furthermore, the disposal of ash generated during incineration requires careful consideration. Depending on the level of contamination, the ash may need to be disposed of in deep-well injection or specially designed hazardous waste landfill sites to prevent further contamination of soil and water.
In conclusion, incineration is a widely used method for hazardous waste disposal through combustion. It offers effective destruction of hazardous materials, reduces waste volume, and can contribute to energy production. However, careful management is crucial to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and prevent potential risks to human health and the environment.
Biological Treatment: Utilizing Living Organisms
One common method of hazardous waste disposal is biological treatment, which involves the use of living organisms to neutralize or break down hazardous waste materials. This method is considered both safe and environmentally friendly, as it avoids the negative impacts associated with other disposal methods such as landfilling, deep-well injection, and incineration.
Biological treatment relies on the natural abilities of microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and algae, to degrade hazardous waste. These organisms are able to metabolize or absorb the waste materials, transforming them into less harmful substances or converting them into non-hazardous byproducts.
This method can be applied to a wide range of hazardous waste types, including organic and inorganic compounds, as well as liquid, gaseous, and solid waste. It is particularly effective for waste materials that are biodegradable.
The process of biological treatment typically involves the following steps:
- Waste Segregation: Hazardous waste is sorted and separated from non-hazardous waste to ensure proper treatment.
- Inoculation: The waste is mixed with a suitable culture of microorganisms, which are chosen based on their ability to degrade the specific type of waste being treated.
- Aeration: Oxygen is introduced into the treatment system to provide the necessary environment for the growth and activity of the microorganisms.
- Monitoring and Control: The process is closely monitored to ensure optimal conditions for the microorganisms, including temperature, pH, and nutrient levels.
- Secondary Treatment: In some cases, a secondary treatment may be required to further reduce the concentration of hazardous substances in the waste.
- Final Disposal: After the waste has been treated and rendered non-hazardous, it can be safely disposed of in landfills or other appropriate facilities.
The use of biological treatment for hazardous waste disposal offers several advantages over other methods. It is a cost-effective solution, as it requires relatively simple infrastructure and can be implemented on a smaller scale compared to technologies like incineration. Furthermore, it does not produce significant air emissions or generate ash residues, reducing its impact on the environment.
Advantages of Biological Treatment Advantages
| Environmental Friendly |
| Cost-effective |
| Applicable to Various Waste Types |
| Reduced Air Emissions and Ash Residues |
Overall, biological treatment offers a safe and efficient approach to hazardous waste disposal, harnessing the power of living organisms to turn hazardous waste into non-hazardous or less harmful substances. With proper implementation and monitoring, this method can contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment.
Chemical Treatment: Transforming Hazardous Substances
Chemical treatment is one of the methods used for the safe disposal of hazardous waste. It involves transforming hazardous substances into less harmful or non-toxic forms through various chemical processes. This method is an effective way to reduce the potential harm posed by hazardous waste to both human health and the environment.
The chemical treatment process can take place in specialized facilities or treatment plants. These facilities are equipped with the necessary equipment and trained personnel to handle hazardous waste safely. The process involves several steps, including:
- Identification and segregation of different types of hazardous waste
- Neutralization of acidic or alkaline waste to adjust pH levels and reduce its corrosiveness
- Chemical reactions to transform hazardous substances into less toxic or non-toxic forms
- Separation and removal of any remaining hazardous components
- Treatment of the resulting waste to meet regulatory requirements
Chemical treatment methods can vary depending on the specific type of hazardous waste being treated. Some common techniques include:
- Incineration: This involves burning hazardous waste at high temperatures, converting it into ash and gases. The resulting ash can then be disposed of in a secure landfill, while the gases can be treated further before release.
- Chemical oxidation: This method uses strong oxidizing agents to chemically react with hazardous substances, breaking them down into less toxic by products.
- Chemical reduction: This technique involves using reducing agents to chemically convert hazardous substances into less harmful forms.
- Biological treatment: Certain hazardous substances can be treated using microorganisms or enzymes that naturally break them down into harmless by products.
After the chemical treatment process, the resulting waste may be subjected to further treatment or recycling, depending on its composition and characteristics. This helps to minimize the amount of waste sent to landfills and promotes a more sustainable approach to waste management.
Overall, chemical treatment plays a crucial role in ensuring the safe disposal of hazardous waste. By transforming hazardous substances into less harmful or non-toxic forms, it helps protect the environment and human health. However, it is important to ensure that chemical treatment facilities follow strict regulations and guidelines to prevent any potential risks or adverse effects associated with the treatment process.
Physical Treatment: Changing Waste Characteristics
Physical treatment is one of the common methods used for hazardous waste disposal. This method involves altering the characteristics of the waste to make it less hazardous or easier to handle and dispose of. There are several physical treatment techniques that can be employed, depending on the specific type and nature of the waste. Some of the commonly used physical treatment methods include:
- Landfill: Landfilling involves burying the waste in specially designed areas. This method is suitable for non-hazardous waste, as well as certain types of hazardous waste that can be safely contained and isolated.
- Deep-well: Deep-well injection involves injecting the waste into a well that is drilled deep into the ground. This method is often used for liquid hazardous waste and helps to prevent the contamination of surface water and groundwater.
- Recycling: Recycling is a physical treatment method that involves recovering and reusing materials from waste. This approach helps to reduce the volume of waste that needs to be disposed of and conserve natural resources.
- Neutralization: Neutralization is a process that involves adjusting the pH level of acidic or alkaline waste to make it less hazardous. This method is commonly used for liquid waste that contains corrosive substances.
- Incineration: Incineration is a physical treatment method that involves burning waste at high temperatures. This process helps to reduce the volume of waste and destroy hazardous substances. However, it is essential to ensure proper air pollution control measures are in place to prevent the release of harmful gases and pollutants.
Physical treatment methods can be effective in changing the characteristics of hazardous waste, making it safer to handle and dispose of. However, it is crucial to consider the specific properties of the waste and choose the appropriate physical treatment method accordingly. Additionally, proper monitoring and compliance with regulatory requirements are necessary to ensure safe and environmentally friendly disposal of hazardous waste.
Recycling: Giving Waste a Second Life
Recycling is one of the most effective and environmentally friendly methods of hazardous waste disposal. It involves the collection and processing of waste materials to create new products or materials, thereby giving waste a second life.
There are various types of recycling methods that can be employed, depending on the nature of the waste. Some common recycling methods include:
- Mechanical Recycling: This method involves the physical separation and processing of waste materials into reusable products. It is typically used for plastics, paper, and metals.
- Chemical Recycling: Chemical recycling involves the use of chemical processes to break down waste materials into their base components for reuse. This method is often employed for organic waste, such as oil and solvents.
- Biological Recycling: This method utilizes natural processes, such as composting or anaerobic digestion, to transform organic waste into nutrient-rich compost or biogas.
Recycling helps to reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills or incineration facilities, which can have significant environmental and health impacts. By recycling waste, valuable resources are conserved, energy consumption is reduced, and greenhouse gas emissions are minimized.
In addition to environmental benefits, recycling also offers economic advantages. It can create jobs in recycling facilities and stimulate the development of a recycling industry. Furthermore, recycled materials can often be sold or used as raw materials in other industries, providing cost savings and reducing the need for virgin resources.
Despite the numerous benefits of recycling, it is important to note that not all hazardous waste can be recycled. Some hazardous materials require specialized methods of disposal, such as neutralization, incineration, or deep-well injection.
In conclusion, recycling is a crucial method of hazardous waste disposal as it gives waste a second life, reduces environmental impacts, conserves resources, and offers economic benefits. By promoting and implementing recycling practices, we can work towards a more sustainable and waste-free future.
Energy Recovery: Generating Power from Waste
Energy recovery is a method of waste disposal that not only helps to reduce the amount of hazardous waste in our environment but also generates power in the process. This method is often used for the disposal of various types of waste, including hazardous materials.
One common energy recovery method is incineration, which involves the burning of waste at high temperatures. This process not only reduces the volume of waste but also produces heat. This heat can be converted into electrical energy, which can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire communities.
Another energy recovery method is deep-well injection, which involves injecting waste deep below the surface of the Earth. This method is commonly used for the disposal of hazardous liquids. As the waste is injected into the well, it can generate geothermal energy, which can be harnessed and used to generate electricity.
Recycling is also a form of energy recovery, as it involves converting waste materials into new products or raw materials. By recycling materials, we reduce the need for extracting and manufacturing new materials, which requires energy. This energy-saving process can help in generating power from waste.
In some cases, waste can be disposed of in landfills, and energy recovery methods can still be utilized. Landfills can be designed with gas collection systems that capture methane, a potent greenhouse gas produced by decomposing waste. The captured methane can then be used as a source of energy, reducing the need for fossil fuels.
Overall, energy recovery methods provide a way to not only dispose of hazardous waste but also generate power in the process. By harnessing the energy within waste materials, we can reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Deep Well Injection: Disposing Underground
Deep well injection is one of the most widely used methods for the disposal of hazardous waste. It involves injecting the waste deep into the ground, where it is stored in specially designed underground wells. This method is chosen when other waste management options, such as recycling, neutralization, incineration, or landfill, are not feasible or environmentally friendly.
The process of deep well injection starts with drilling a well that reaches a depth of thousands of feet below the ground surface. The well is lined with multiple layers of protective material to prevent any leakage or contamination of the surrounding soil and groundwater. Once the well is prepared, the waste is injected into it under high pressure.
The waste is injected into porous rock formations, such as sandstone or limestone, which have the capacity to contain and trap the waste. These formations act as natural barriers and minimize the risk of leakage or migration of the waste. The waste is typically injected into the well in a controlled manner, allowing it to disperse and distribute within the underground formation.
Deep well injection is considered a safe and effective method of hazardous waste disposal, as long as it is properly regulated and monitored. The injection wells are subject to strict regulatory requirements to ensure their integrity and prevent any environmental harm. Regular monitoring and testing of the well and the surrounding area are conducted to detect and address any potential issues.
- Advantages of Deep Well Injection:
- Provides a long-term solution for the disposal of hazardous waste.
- Minimizes the risk of contamination to the soil and groundwater.
- Allows for the disposal of large volumes of waste in a compact space.
- Reduces the need for transportation of waste over long distances.
- Disadvantages of Deep Well Injection:
- There is a potential risk of seismic activity due to deep well injection.
- There may be public concerns about the safety and environmental impact of the method.
- Requires careful selection of injection sites and proper geologic characterization.
- May require extensive monitoring and maintenance to ensure long-term safety.
In conclusion, deep well injection is a commonly used method for the disposal of hazardous waste. It provides a safe and environmentally friendly solution when other methods are not feasible. Proper regulation and monitoring are essential to ensure the integrity of the injection wells and prevent any potential harm to the environment.
Encapsulation: Isolating Hazardous Materials
Encapsulation is one of the common methods used for the disposal of hazardous waste. It involves isolating the hazardous materials in a different substance to prevent them from coming into contact with the environment and causing harm. This method is considered safe and effective for managing and disposing of various types of hazardous waste.
The process of encapsulation typically involves mixing the hazardous waste with a solid binder material, which creates a solid block or matrix. This solid block effectively contains the hazardous materials and prevents them from leaching or spreading into the surrounding soil or water sources.
There are several advantages of encapsulation as a method of hazardous waste disposal:
- Containment: Encapsulation provides a high level of containment for hazardous materials, minimizing the risk of environmental contamination.
- Ease of handling: The solidified form of encapsulated waste makes it easier to handle and transport, reducing the risk of accidental spills.
- Long-term stability: The solid block created through encapsulation ensures the long-term stability of hazardous waste. It can withstand various environmental conditions and does not degrade or release toxins over time.
There are different methods of encapsulation depending on the type of hazardous waste and the desired level of isolation. Some of the common methods include:
- Deep-well encapsulation: This method involves injecting the hazardous waste into deep underground wells that are specifically designed for storing and isolating hazardous materials. The deep-well encapsulation ensures that the waste is securely contained deep below the surface.
- Neutralization and solidification: This method involves neutralizing the hazardous waste with chemicals to make it less harmful and then solidifying it with a binder material. The solidified waste can then be safely stored or disposed of in a landfill.
- Encapsulation for recycling: In some cases, hazardous waste can be encapsulated to allow for safer recycling processes. The encapsulation process ensures that the hazardous materials are contained and do not pose a risk during the recycling process.
Overall, encapsulation is an effective method for isolating hazardous materials and preventing them from causing harm to the environment. It provides a safe and environmentally friendly solution for the disposal of hazardous waste.
Neutralization: Safely Neutralizing Hazardous Chemicals

Neutralization is one of the common methods used for the safe disposal of hazardous chemicals. It involves treating these chemicals with substances that can neutralize their harmful effects and make them less dangerous to handle and dispose of.
Hazardous chemicals, such as acids and bases, can pose serious risks to human health and the environment if not properly managed. The traditional methods of hazardous waste disposal, such as incineration and landfill, may not be suitable for these chemicals as they can release harmful pollutants into the air or contaminate the soil and groundwater.
Neutralization offers a more environmentally friendly solution for the disposal of hazardous chemicals. By neutralizing these chemicals, their harmful properties can be eliminated or significantly reduced. This process involves mixing the hazardous chemicals with substances that have opposite properties, such as acids with bases or bases with acids.
During neutralization, a chemical reaction occurs between the hazardous chemicals and the neutralizing agents. This reaction results in the formation of less harmful compounds that are easier to handle and dispose of. The neutralized chemicals can then be safely stored, treated, or even recycled, depending on their nature and composition.
Neutralization can be carried out through various methods, including batch processes, continuous processes, and on-site treatment systems. These methods often involve the use of specialized equipment and trained personnel to ensure the safe and effective neutralization of hazardous chemicals.
It is important to note that neutralization may not be suitable for all types of hazardous chemicals. Some chemicals may require specific treatment methods, such as deep-well disposal or specialized recycling processes. Therefore, it is crucial to properly identify the nature of the hazardous chemicals before deciding on the most appropriate disposal method.
In conclusion, neutralization is an important method for the safe disposal of hazardous chemicals. It allows for the elimination or reduction of the harmful properties of these chemicals, making them easier to handle and dispose of. However, it is essential to ensure that neutralization is the appropriate method for a specific type of hazardous chemical and to follow proper protocols and guidelines to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the process.
Stabilization: Reducing Hazardous Properties
One of the common methods of hazardous waste disposal is stabilization. Stabilization refers to a process that aims to reduce the hazardous properties of waste, making it safer for disposal in landfills or other methods.
When waste is stabilized, it means that its chemical and physical properties are altered to minimize any potential risks. This is achieved through various techniques, such as:
- Neutralization: This method involves treating the waste with chemicals to neutralize its acidity or alkalinity. By adjusting the pH level, the waste becomes less hazardous and more stable.
- Recycling: Recycling hazardous waste is another form of stabilization. By converting waste materials into useful products or raw materials, the hazardous properties are eliminated or reduced.
- Chemical Fixation: Chemical fixation involves adding chemicals to the waste to create chemical reactions that turn hazardous substances into less harmful or inert compounds. This reduces the risk of contamination and makes the waste more stable.
Stabilization is an important step in the hazardous waste disposal process, as it helps to minimize the potential risks associated with handling and storing hazardous waste. It ensures that the waste is less likely to pose a threat to human health or the environment.
After stabilization, the waste can be disposed of in a landfill, deep-well injection, or through incineration. These methods are chosen based on the characteristics of the waste and the level of stabilization achieved.
Method Description
| Landfill | Stabilized waste is placed in a specially designed landfill where it is safely contained and monitored to prevent leakage or contamination. |
| Deep-well Injection | Stabilized waste is injected deep underground into specially constructed wells, where it is isolated from the environment. |
| Incineration | Stabilized waste is burned at high temperatures, reducing it to ash and gases. Advanced incineration technologies can further minimize any remaining hazardous properties. |
Overall, stabilization plays a crucial role in hazardous waste management. It reduces the hazardous properties of waste, making it safer for disposal and minimizing the potential risks to human health and the environment.
Question-answer:
What are the common methods of hazardous waste disposal?
The common methods of hazardous waste disposal include landfilling, incineration, recycling, and chemical treatment.
How do these methods ensure safe and environmentally friendly solutions?
Landfilling involves burying the waste in a designated area, ensuring that it does not contaminate the surrounding environment. Incineration involves burning the waste at high temperatures, effectively neutralizing hazardous substances. Recycling allows for the reutilization of materials, reducing the need for new production. Chemical treatment involves treating the waste to reduce or eliminate its hazardous properties.
What are the advantages of landfilling hazardous waste?
The advantages of landfilling hazardous waste include its relative simplicity and cost-effectiveness compared to other methods. When properly designed and managed, landfills can effectively contain and isolate the waste, preventing contamination of soil and water sources.
Are there any disadvantages to incineration as a method of hazardous waste disposal?
Yes, there are some disadvantages to incineration. The process can release harmful pollutants into the air, such as dioxins and heavy metals. Additionally, incineration requires high energy inputs and can be expensive to implement.
Can hazardous waste be recycled?
Yes, hazardous waste can be recycled. Some materials, such as certain types of batteries or electronic waste, can be processed and reused. Recycling hazardous waste reduces the need for new production and conserves resources.
What are some common methods of hazardous waste disposal?
Some common methods of hazardous waste disposal include landfilling, incineration, recycling, and treatment. These methods are used to ensure safe and environmentally friendly solutions for hazardous waste disposal.
Why is it important to ensure safe and environmentally friendly solutions for hazardous waste disposal?
It is important to ensure safe and environmentally friendly solutions for hazardous waste disposal because hazardous waste can pose serious risks to human health and the environment. Improper disposal can lead to contamination of soil, water, and air, which can have long-lasting negative effects. Proper disposal methods help minimize these risks and protect both human and environmental health.






